-
JUnit5 확장 모델테스트/Junit5 2021. 2. 8. 16:20
만약 테스트 시간이 오래 걸리는 테스트를 찾아 @SlowTest 어노테이션을 붙여주는 Extention모델을 구현한다 가정하자.
이러한 기능을 하는 JavaClass를 구현하고, 테스트 클레스에서 등록해줄 때, 필요한 것은 @ExtendWith 애노테이션이 필요하다.
바로 실습해보자.
예제코드 1. 테스트 시간이 일정시간 지나면 @SlowTest 태깅을 고려해주는 FindSlowTestExtension 구현하기
Exteion 모델을 구현하기 위해서 다음 Interface를 알아둘 필요가 있다.
BeforeTestExecutionCallback, AfterTestExecutionCallback 은 다음과 같이 설명되어 있다.
BeforeTestExecutionCallback (JUnit 5.7.1 API)
BeforeTestExecutionCallback defines the API for Extensions that wish to provide additional behavior to tests immediately before an individual test is executed but after any user-defined setup methods (e.g., @BeforeEach methods) have been executed for that
junit.org
BeforeTestExecutionCallback defines the API for Extensions that wish to provide additional behavior to tests immediately before an individual test is executed but after any user-defined setup methods (e.g., @BeforeEachmethods) have been executed for that test.
즉 각각의 테스트를 전 후로 테스트의 시간을 측정하고 걸리는 시간을 구해내야하기 때문에 이와같은 인터페이스를 사용해야한다.
또한 메소드에 beforeTestExecution을 구현해주어야 한다. 이 메소드에선 테스트를 실행하기전 호출되는 콜백함수로 실제 원하는 기능을 여기에다 구현해주어야 한다.
또한 Before, AfterTestExecution 메소드에 ExtensionContext 파라미터가 있는데, 이 파라미터를 통해 테스트 클레스이름과 메서드 이름을 추출한다 또한 테스트 데이터를 저장하고, 추출하는 기능을 담당하는 getStore()메소드를 사용할 것이다.
package com.example.junittest; import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.AfterTestExecutionCallback; import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.BeforeTestExecutionCallback; import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtensionContext; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class FindSlowTestExtension implements BeforeTestExecutionCallback, AfterTestExecutionCallback { private static final long THRESHOLD = 1000L; @Override public void beforeTestExecution(ExtensionContext extensionContext) throws Exception { ExtensionContext.Store store = getStore(extensionContext); store.put("START_TIME",System.currentTimeMillis()); } @Override public void afterTestExecution(ExtensionContext extensionContext) throws Exception { Method method = extensionContext.getRequiredTestMethod(); slowTest annotation = method.getAnnotation(slowTest.class); String testMethod = extensionContext.getRequiredTestMethod().getName(); ExtensionContext.Store store = getStore(extensionContext); Long start_time = store.get("START_TIME", long.class); long duration = System.currentTimeMillis()-start_time; if(duration>THRESHOLD && annotation==null){ System.out.printf("please consider mark method[%s] with @slowTest. \n",testMethod); } } private ExtensionContext.Store getStore(ExtensionContext extensionContext) { String ClassName= extensionContext.getRequiredTestClass().getClass().getName(); //requiredTestClass는 현재 테스트의 클레스 이름 String testMethod = extensionContext.getRequiredTestMethod().getName(); ExtensionContext.Store store = extensionContext.getStore(ExtensionContext.Namespace.create(ClassName,testMethod)); return store; } }
2.확장모델 적용하기
1)@ExtendWith로 모델 등록하기
package com.example.junittest; import org.junit.jupiter.api.*; import org.junit.jupiter.api.condition.DisabledOnJre; import org.junit.jupiter.api.condition.DisabledOnOs; import org.junit.jupiter.api.condition.JRE; import org.junit.jupiter.api.condition.OS; import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith; @ExtendWith(FindSlowTestExtension.class) @DisplayName("스터디 클레스") class StudyTest { int value = 1; @Test void create_new_study_test() throws InterruptedException { Thread.sleep(1005); System.out.println(value); value++; System.out.println(this); Class<Long> longClass = long.class; } @Test void create_again_study_test() { System.out.println(value); value++; System.out.println(this); } }위 소스코드를 보면 1005ms간 강제적으로 메소드를 멈추게했다.
결과는 다음과 같다.
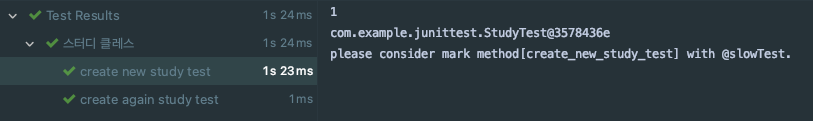
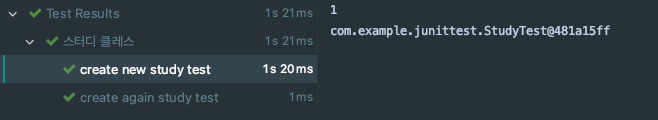
조언대로 시간이 걸리는 테스트 메소드에 사용자가 정의한 slowTest 어노테이션을 붙이면 다음과 같은 결과가 나온다.
2)@RegisterExtension으로 확장 모델에 구체적인 조건 조작하기
좀 더 구체적인 동작이라 함은 본 글에서 기본생성자를 만들어 THRESHOLD값을 테스트마다 값을 할당한다고 가정하자.
변경된 소스는 다음과같이 확장모델에 기본생성자를 만들어주었다.
package com.example.junittest; import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.AfterTestExecutionCallback; import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.BeforeTestExecutionCallback; import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtensionContext; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class FindSlowTestExtension implements BeforeTestExecutionCallback, AfterTestExecutionCallback { private long THRESHOLD ; private FindSlowTestExtension(long THRESHOLD){ this.THRESHOLD = THRESHOLD; } @Override public void beforeTestExecution(ExtensionContext extensionContext) throws Exception { ExtensionContext.Store store = getStore(extensionContext); store.put("START_TIME",System.currentTimeMillis()); } @Override public void afterTestExecution(ExtensionContext extensionContext) throws Exception { Method method = extensionContext.getRequiredTestMethod(); slowTest annotation = method.getAnnotation(slowTest.class); String testMethod = extensionContext.getRequiredTestMethod().getName(); ExtensionContext.Store store = getStore(extensionContext); Long start_time = store.get("START_TIME", long.class); long duration = System.currentTimeMillis()-start_time; if(duration>THRESHOLD && annotation==null){ System.out.printf("please consider mark method[%s] with @slowTest. \n",testMethod); } } private ExtensionContext.Store getStore(ExtensionContext extensionContext) { String ClassName= extensionContext.getRequiredTestClass().getClass().getName(); //requiredTestClass는 현재 테스트의 클레스 이름 String testMethod = extensionContext.getRequiredTestMethod().getName(); ExtensionContext.Store store = extensionContext.getStore(ExtensionContext.Namespace.create(ClassName,testMethod)); return store; } }이렇게 하면 확장모델을 추가할때, 기본생성자를 호출해 값을 할당해야 인스턴스가 생성된다. 따라서 @RegisterExtension이 필요하다.
package com.example.junittest; import org.junit.jupiter.api.*; import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.RegisterExtension; @DisplayName("스터디 클레스") class StudyTest { int value = 1; @RegisterExtension static FindSlowTestExtension findSlowTestExtension = new FindSlowTestExtension(1000L); @Test void create_new_study_test() throws InterruptedException { Thread.sleep(1005); System.out.println(value); value++; System.out.println(this); Class<Long> longClass = long.class; } @Test void create_again_study_test() { System.out.println(value); value++; System.out.println(this); } }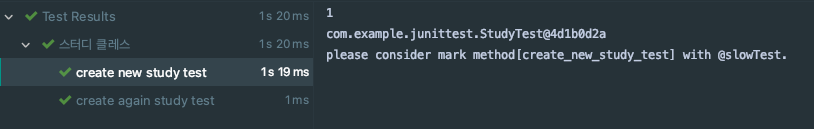
'테스트 > Junit5' 카테고리의 다른 글
Junit5에서 Junit4마이그레이션 하기 (0) 2021.02.08 properties파일로 JUnit5 설정하기 (0) 2021.02.08 테스트 순서 (0) 2021.02.06 테스트 인스턴스 (0) 2021.02.06 테스트 반복하기2 @ParameterizedTest이용한 추가 방법 (0) 2021.02.02